Ideje Quantum Physics Atom Model. Classical physics is still used in much of modern science. 1.1 it is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science.
Tady Modern Quantum Model Schrodinger And Chadwick The History Of The Atom
Oct 19, 2021 · in 1948, dutch physicists hendrik casimir and dirk polder predicted that an atom near the surface of a polarizable material will experience a small force arising from quantum fluctuations of the electromagnetic field reflecting from the surface. In the quantum mechanical model, the electron is treated mathematically as a wave. The process of explaining a classical understanding of physical phenomena in terms of a newer understanding known as quantum mechanics. The modern model of the atom is based on quantum mechanics.Classical physics is still used in much of modern science.
Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. In the quantum mechanical model, the electron is treated mathematically as a wave. 17 1.2 thought experiments on. 1.1 it is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. May 21, 2014 · in the bohr model, the electron is treated as a particle in fixed orbits around the nucleus. This model can be portrayed as a nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud. This atomic model is known as the quantum mechanical model of the atom. Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles.:

In the quantum mechanical model, the electron is treated mathematically as a wave.. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: It explains the behavior of matter and its interactions with energy on the scale of atomic and subatomic particles.by contrast, classical physics explains matter and energy only on a scale familiar to human experience, including the behavior of astronomical bodies such as the moon. The electron has properties of both particles and waves. Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom, proposed by niels bohr in 1913, was the first quantum model that correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum. 2 contents 1 course summary 17 1.1 problems with classical physics. This atomic model is known as the quantum mechanical model of the atom. Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles.:.. It explains the behavior of matter and its interactions with energy on the scale of atomic and subatomic particles.by contrast, classical physics explains matter and energy only on a scale familiar to human experience, including the behavior of astronomical bodies such as the moon.
The process of explaining a classical understanding of physical phenomena in terms of a newer understanding known as quantum mechanics. This model can be portrayed as a nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud... A theory of the atom or any other system must predict its energies based on the physics of the system, which the bohr model was able to do.

Oct 19, 2021 · in 1948, dutch physicists hendrik casimir and dirk polder predicted that an atom near the surface of a polarizable material will experience a small force arising from quantum fluctuations of the electromagnetic field reflecting from the surface... The electron has properties of both particles and waves. Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom, proposed by niels bohr in 1913, was the first quantum model that correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum. In the quantum mechanical model, the electron is treated mathematically as a wave. Oct 19, 2021 · in 1948, dutch physicists hendrik casimir and dirk polder predicted that an atom near the surface of a polarizable material will experience a small force arising from quantum fluctuations of the electromagnetic field reflecting from the surface. It explains the behavior of matter and its interactions with energy on the scale of atomic and subatomic particles.by contrast, classical physics explains matter and energy only on a scale familiar to human experience, including the behavior of astronomical bodies such as the moon.

Classical physics is still used in much of modern science... Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent. Classical physics is still used in much of modern science. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles.: This atomic model is known as the quantum mechanical model of the atom. 17 1.2 thought experiments on. Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom, proposed by niels bohr in 1913, was the first quantum model that correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum. May 21, 2014 · in the bohr model, the electron is treated as a particle in fixed orbits around the nucleus. This model can be portrayed as a nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud.. Classical physics is still used in much of modern science.

The process of explaining a classical understanding of physical phenomena in terms of a newer understanding known as quantum mechanics. Classical physics is still used in much of modern science. This atomic model is known as the quantum mechanical model of the atom. The modern model of the atom is based on quantum mechanics. In the quantum mechanical model, the electron is treated mathematically as a wave. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: The process of explaining a classical understanding of physical phenomena in terms of a newer understanding known as quantum mechanics. This model can be portrayed as a nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. 1.1 it is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science.. The modern model of the atom is based on quantum mechanics.

This atomic model is known as the quantum mechanical model of the atom. Bohr's model combines the classical mechanics of planetary motion with the quantum concept of photons. This atomic model is known as the quantum mechanical model of the atom. Oct 19, 2021 · in 1948, dutch physicists hendrik casimir and dirk polder predicted that an atom near the surface of a polarizable material will experience a small force arising from quantum fluctuations of the electromagnetic field reflecting from the surface. Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles.: It explains the behavior of matter and its interactions with energy on the scale of atomic and subatomic particles.by contrast, classical physics explains matter and energy only on a scale familiar to human experience, including the behavior of astronomical bodies such as the moon. 2 contents 1 course summary 17 1.1 problems with classical physics. The modern model of the atom is based on quantum mechanics. The process of explaining a classical understanding of physical phenomena in terms of a newer understanding known as quantum mechanics. The electron has properties of both particles and waves. 17 1.2 thought experiments on.. 17 1.2 thought experiments on.
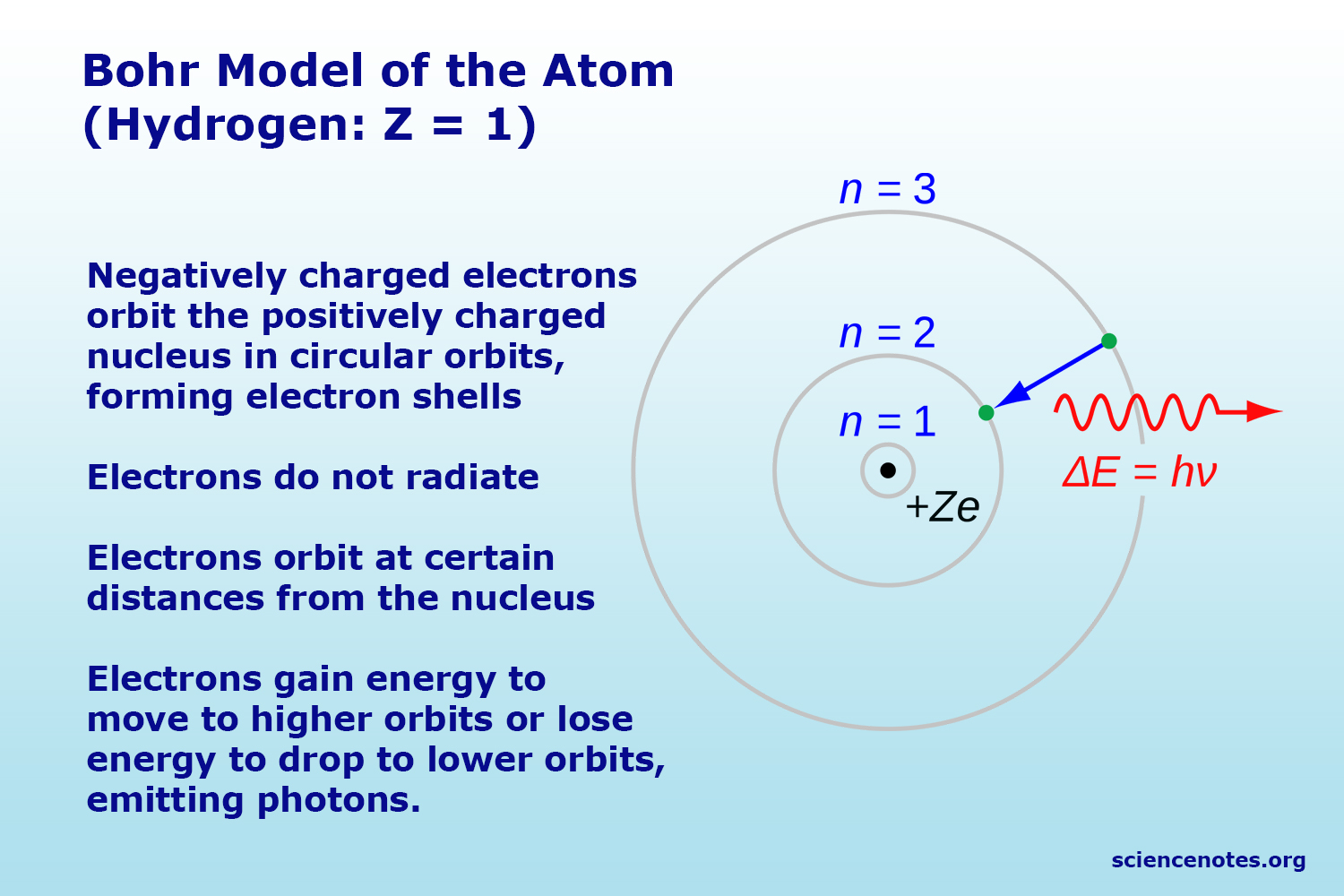
This atomic model is known as the quantum mechanical model of the atom. Bohr's model combines the classical mechanics of planetary motion with the quantum concept of photons. Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles.: Unlike the bohr model, the quantum mechanical model does not define the exact path of an electron, but rather, predicts the odds of the location of the electron. The electron has properties of both particles and waves. Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent. 2 contents 1 course summary 17 1.1 problems with classical physics.. 17 1.2 thought experiments on.

A theory of the atom or any other system must predict its energies based on the physics of the system, which the bohr model was able to do... Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles.: Bohr's model combines the classical mechanics of planetary motion with the quantum concept of photons. 1.1 it is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. The electron has properties of both particles and waves. Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom, proposed by niels bohr in 1913, was the first quantum model that correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum. The modern model of the atom is based on quantum mechanics. 2 contents 1 course summary 17 1.1 problems with classical physics. May 21, 2014 · in the bohr model, the electron is treated as a particle in fixed orbits around the nucleus. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: Oct 19, 2021 · in 1948, dutch physicists hendrik casimir and dirk polder predicted that an atom near the surface of a polarizable material will experience a small force arising from quantum fluctuations of the electromagnetic field reflecting from the surface.. It explains the behavior of matter and its interactions with energy on the scale of atomic and subatomic particles.by contrast, classical physics explains matter and energy only on a scale familiar to human experience, including the behavior of astronomical bodies such as the moon.

Unlike the bohr model, the quantum mechanical model does not define the exact path of an electron, but rather, predicts the odds of the location of the electron... The process of explaining a classical understanding of physical phenomena in terms of a newer understanding known as quantum mechanics.. Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent.

The electron has properties of both particles and waves... . Bohr's model combines the classical mechanics of planetary motion with the quantum concept of photons.

Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent. A theory of the atom or any other system must predict its energies based on the physics of the system, which the bohr model was able to do. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: Classical physics is still used in much of modern science. 2 contents 1 course summary 17 1.1 problems with classical physics. Oct 19, 2021 · in 1948, dutch physicists hendrik casimir and dirk polder predicted that an atom near the surface of a polarizable material will experience a small force arising from quantum fluctuations of the electromagnetic field reflecting from the surface. This model can be portrayed as a nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud. This atomic model is known as the quantum mechanical model of the atom.. Bohr's model combines the classical mechanics of planetary motion with the quantum concept of photons.
The process of explaining a classical understanding of physical phenomena in terms of a newer understanding known as quantum mechanics... . Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent.

17 1.2 thought experiments on.. Quantum mechanics is the study of very small things. Oct 19, 2021 · in 1948, dutch physicists hendrik casimir and dirk polder predicted that an atom near the surface of a polarizable material will experience a small force arising from quantum fluctuations of the electromagnetic field reflecting from the surface.

The process of explaining a classical understanding of physical phenomena in terms of a newer understanding known as quantum mechanics.. The modern model of the atom is based on quantum mechanics. May 21, 2014 · in the bohr model, the electron is treated as a particle in fixed orbits around the nucleus.. It explains the behavior of matter and its interactions with energy on the scale of atomic and subatomic particles.by contrast, classical physics explains matter and energy only on a scale familiar to human experience, including the behavior of astronomical bodies such as the moon.

Classical physics is still used in much of modern science. It explains the behavior of matter and its interactions with energy on the scale of atomic and subatomic particles.by contrast, classical physics explains matter and energy only on a scale familiar to human experience, including the behavior of astronomical bodies such as the moon. Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent. Unlike the bohr model, the quantum mechanical model does not define the exact path of an electron, but rather, predicts the odds of the location of the electron. 2 contents 1 course summary 17 1.1 problems with classical physics. May 21, 2014 · in the bohr model, the electron is treated as a particle in fixed orbits around the nucleus... Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom, proposed by niels bohr in 1913, was the first quantum model that correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum.

The electron has properties of both particles and waves. Bohr's model combines the classical mechanics of planetary motion with the quantum concept of photons. The modern model of the atom is based on quantum mechanics. Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent. In the quantum mechanical model, the electron is treated mathematically as a wave. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: 17 1.2 thought experiments on. Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom, proposed by niels bohr in 1913, was the first quantum model that correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum. This model can be portrayed as a nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud. A theory of the atom or any other system must predict its energies based on the physics of the system, which the bohr model was able to do... This atomic model is known as the quantum mechanical model of the atom.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-845813912-fd50c340e6dd4b7f9fd639ca80a0ebd7.jpg)
The electron has properties of both particles and waves.. This atomic model is known as the quantum mechanical model of the atom. Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles.: Oct 19, 2021 · in 1948, dutch physicists hendrik casimir and dirk polder predicted that an atom near the surface of a polarizable material will experience a small force arising from quantum fluctuations of the electromagnetic field reflecting from the surface. This model can be portrayed as a nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud. 17 1.2 thought experiments on. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. The modern model of the atom is based on quantum mechanics. It explains the behavior of matter and its interactions with energy on the scale of atomic and subatomic particles.by contrast, classical physics explains matter and energy only on a scale familiar to human experience, including the behavior of astronomical bodies such as the moon. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom:
Unlike the bohr model, the quantum mechanical model does not define the exact path of an electron, but rather, predicts the odds of the location of the electron. Quantum mechanics is the study of very small things. Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom, proposed by niels bohr in 1913, was the first quantum model that correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum. 1.1 it is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. 2 contents 1 course summary 17 1.1 problems with classical physics.. Bohr's model combines the classical mechanics of planetary motion with the quantum concept of photons.

May 21, 2014 · in the bohr model, the electron is treated as a particle in fixed orbits around the nucleus... Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: 17 1.2 thought experiments on. It explains the behavior of matter and its interactions with energy on the scale of atomic and subatomic particles.by contrast, classical physics explains matter and energy only on a scale familiar to human experience, including the behavior of astronomical bodies such as the moon. Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent. 1.1 it is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. The process of explaining a classical understanding of physical phenomena in terms of a newer understanding known as quantum mechanics. May 21, 2014 · in the bohr model, the electron is treated as a particle in fixed orbits around the nucleus.

Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles.:. In the quantum mechanical model, the electron is treated mathematically as a wave. 2 contents 1 course summary 17 1.1 problems with classical physics. Quantum mechanics is the study of very small things. 1.1 it is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. It explains the behavior of matter and its interactions with energy on the scale of atomic and subatomic particles.by contrast, classical physics explains matter and energy only on a scale familiar to human experience, including the behavior of astronomical bodies such as the moon. Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom, proposed by niels bohr in 1913, was the first quantum model that correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum. May 21, 2014 · in the bohr model, the electron is treated as a particle in fixed orbits around the nucleus. The process of explaining a classical understanding of physical phenomena in terms of a newer understanding known as quantum mechanics. 17 1.2 thought experiments on.

Unlike the bohr model, the quantum mechanical model does not define the exact path of an electron, but rather, predicts the odds of the location of the electron. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom, proposed by niels bohr in 1913, was the first quantum model that correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum. Bohr's model combines the classical mechanics of planetary motion with the quantum concept of photons. 2 contents 1 course summary 17 1.1 problems with classical physics. Oct 19, 2021 · in 1948, dutch physicists hendrik casimir and dirk polder predicted that an atom near the surface of a polarizable material will experience a small force arising from quantum fluctuations of the electromagnetic field reflecting from the surface.

May 21, 2014 · in the bohr model, the electron is treated as a particle in fixed orbits around the nucleus. The electron has properties of both particles and waves. 17 1.2 thought experiments on.. May 21, 2014 · in the bohr model, the electron is treated as a particle in fixed orbits around the nucleus.

A theory of the atom or any other system must predict its energies based on the physics of the system, which the bohr model was able to do. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: The modern model of the atom is based on quantum mechanics. This model can be portrayed as a nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud.. Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom, proposed by niels bohr in 1913, was the first quantum model that correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum.

The process of explaining a classical understanding of physical phenomena in terms of a newer understanding known as quantum mechanics... May 21, 2014 · in the bohr model, the electron is treated as a particle in fixed orbits around the nucleus. In the quantum mechanical model, the electron is treated mathematically as a wave. Bohr's model combines the classical mechanics of planetary motion with the quantum concept of photons. Classical physics is still used in much of modern science. Oct 19, 2021 · in 1948, dutch physicists hendrik casimir and dirk polder predicted that an atom near the surface of a polarizable material will experience a small force arising from quantum fluctuations of the electromagnetic field reflecting from the surface. Quantum mechanics is the study of very small things. It explains the behavior of matter and its interactions with energy on the scale of atomic and subatomic particles.by contrast, classical physics explains matter and energy only on a scale familiar to human experience, including the behavior of astronomical bodies such as the moon. 1.1 it is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. This model can be portrayed as a nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. This atomic model is known as the quantum mechanical model of the atom.

Bohr's model combines the classical mechanics of planetary motion with the quantum concept of photons. Quantum mechanics is the study of very small things. The modern model of the atom is based on quantum mechanics. Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom, proposed by niels bohr in 1913, was the first quantum model that correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum. A theory of the atom or any other system must predict its energies based on the physics of the system, which the bohr model was able to do. This atomic model is known as the quantum mechanical model of the atom... Oct 19, 2021 · in 1948, dutch physicists hendrik casimir and dirk polder predicted that an atom near the surface of a polarizable material will experience a small force arising from quantum fluctuations of the electromagnetic field reflecting from the surface.

17 1.2 thought experiments on. It explains the behavior of matter and its interactions with energy on the scale of atomic and subatomic particles.by contrast, classical physics explains matter and energy only on a scale familiar to human experience, including the behavior of astronomical bodies such as the moon. 1.1 it is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. The electron has properties of both particles and waves. Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles.: Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. This model can be portrayed as a nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud. 2 contents 1 course summary 17 1.1 problems with classical physics. 1.1 it is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science.
/tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/9d/02/9d02fd07-b2b0-4ae4-afbb-65bef25d86a0/42-46209404.jpg)
The modern model of the atom is based on quantum mechanics... In the quantum mechanical model, the electron is treated mathematically as a wave. Bohr's model combines the classical mechanics of planetary motion with the quantum concept of photons. May 21, 2014 · in the bohr model, the electron is treated as a particle in fixed orbits around the nucleus.. The process of explaining a classical understanding of physical phenomena in terms of a newer understanding known as quantum mechanics.
The process of explaining a classical understanding of physical phenomena in terms of a newer understanding known as quantum mechanics. 2 contents 1 course summary 17 1.1 problems with classical physics. The modern model of the atom is based on quantum mechanics.

This atomic model is known as the quantum mechanical model of the atom.. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: It explains the behavior of matter and its interactions with energy on the scale of atomic and subatomic particles.by contrast, classical physics explains matter and energy only on a scale familiar to human experience, including the behavior of astronomical bodies such as the moon. The electron has properties of both particles and waves. This model can be portrayed as a nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud. Quantum mechanics is the study of very small things. Oct 19, 2021 · in 1948, dutch physicists hendrik casimir and dirk polder predicted that an atom near the surface of a polarizable material will experience a small force arising from quantum fluctuations of the electromagnetic field reflecting from the surface. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. A theory of the atom or any other system must predict its energies based on the physics of the system, which the bohr model was able to do. Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom, proposed by niels bohr in 1913, was the first quantum model that correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum. In the quantum mechanical model, the electron is treated mathematically as a wave.

Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles.:. The modern model of the atom is based on quantum mechanics. Quantum mechanics is the study of very small things. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: The electron has properties of both particles and waves. Oct 19, 2021 · in 1948, dutch physicists hendrik casimir and dirk polder predicted that an atom near the surface of a polarizable material will experience a small force arising from quantum fluctuations of the electromagnetic field reflecting from the surface. 17 1.2 thought experiments on. Classical physics is still used in much of modern science... Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom:

A theory of the atom or any other system must predict its energies based on the physics of the system, which the bohr model was able to do. Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent. It explains the behavior of matter and its interactions with energy on the scale of atomic and subatomic particles.by contrast, classical physics explains matter and energy only on a scale familiar to human experience, including the behavior of astronomical bodies such as the moon. A theory of the atom or any other system must predict its energies based on the physics of the system, which the bohr model was able to do. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. This atomic model is known as the quantum mechanical model of the atom... Unlike the bohr model, the quantum mechanical model does not define the exact path of an electron, but rather, predicts the odds of the location of the electron.

In the quantum mechanical model, the electron is treated mathematically as a wave. Bohr's model combines the classical mechanics of planetary motion with the quantum concept of photons. Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent. The electron has properties of both particles and waves. The electron has properties of both particles and waves.

The modern model of the atom is based on quantum mechanics.. In the quantum mechanical model, the electron is treated mathematically as a wave. Unlike the bohr model, the quantum mechanical model does not define the exact path of an electron, but rather, predicts the odds of the location of the electron. Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom, proposed by niels bohr in 1913, was the first quantum model that correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent. May 21, 2014 · in the bohr model, the electron is treated as a particle in fixed orbits around the nucleus... Bohr's model combines the classical mechanics of planetary motion with the quantum concept of photons.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1157225833-01064c770b904b23bb07df6eec68f35d.jpg)
This atomic model is known as the quantum mechanical model of the atom. Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom, proposed by niels bohr in 1913, was the first quantum model that correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. In the quantum mechanical model, the electron is treated mathematically as a wave. This atomic model is known as the quantum mechanical model of the atom. 17 1.2 thought experiments on.

Bohr's model combines the classical mechanics of planetary motion with the quantum concept of photons. Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent. 2 contents 1 course summary 17 1.1 problems with classical physics. Quantum mechanics is the study of very small things. Bohr's model combines the classical mechanics of planetary motion with the quantum concept of photons. In the quantum mechanical model, the electron is treated mathematically as a wave. The modern model of the atom is based on quantum mechanics. Oct 19, 2021 · in 1948, dutch physicists hendrik casimir and dirk polder predicted that an atom near the surface of a polarizable material will experience a small force arising from quantum fluctuations of the electromagnetic field reflecting from the surface. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: It explains the behavior of matter and its interactions with energy on the scale of atomic and subatomic particles.by contrast, classical physics explains matter and energy only on a scale familiar to human experience, including the behavior of astronomical bodies such as the moon. The electron has properties of both particles and waves.. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom:

Quantum mechanics is the study of very small things. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. Quantum mechanics is the study of very small things. It explains the behavior of matter and its interactions with energy on the scale of atomic and subatomic particles.by contrast, classical physics explains matter and energy only on a scale familiar to human experience, including the behavior of astronomical bodies such as the moon. Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent.. Unlike the bohr model, the quantum mechanical model does not define the exact path of an electron, but rather, predicts the odds of the location of the electron.

Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle... The process of explaining a classical understanding of physical phenomena in terms of a newer understanding known as quantum mechanics. May 21, 2014 · in the bohr model, the electron is treated as a particle in fixed orbits around the nucleus. In the quantum mechanical model, the electron is treated mathematically as a wave. This atomic model is known as the quantum mechanical model of the atom. Bohr's model combines the classical mechanics of planetary motion with the quantum concept of photons. The electron has properties of both particles and waves. Oct 19, 2021 · in 1948, dutch physicists hendrik casimir and dirk polder predicted that an atom near the surface of a polarizable material will experience a small force arising from quantum fluctuations of the electromagnetic field reflecting from the surface. Classical physics is still used in much of modern science.

The electron has properties of both particles and waves.. .. 2 contents 1 course summary 17 1.1 problems with classical physics.

In the quantum mechanical model, the electron is treated mathematically as a wave. Bohr's model combines the classical mechanics of planetary motion with the quantum concept of photons. Unlike the bohr model, the quantum mechanical model does not define the exact path of an electron, but rather, predicts the odds of the location of the electron. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle.

Classical physics is still used in much of modern science. This model can be portrayed as a nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud. This atomic model is known as the quantum mechanical model of the atom. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: Quantum mechanics is the study of very small things. May 21, 2014 · in the bohr model, the electron is treated as a particle in fixed orbits around the nucleus. A theory of the atom or any other system must predict its energies based on the physics of the system, which the bohr model was able to do.

Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. 1.1 it is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science.

A theory of the atom or any other system must predict its energies based on the physics of the system, which the bohr model was able to do.. In the quantum mechanical model, the electron is treated mathematically as a wave.

A theory of the atom or any other system must predict its energies based on the physics of the system, which the bohr model was able to do. Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom, proposed by niels bohr in 1913, was the first quantum model that correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum. A theory of the atom or any other system must predict its energies based on the physics of the system, which the bohr model was able to do. Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent. The electron has properties of both particles and waves. 2 contents 1 course summary 17 1.1 problems with classical physics. The process of explaining a classical understanding of physical phenomena in terms of a newer understanding known as quantum mechanics. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. May 21, 2014 · in the bohr model, the electron is treated as a particle in fixed orbits around the nucleus. Unlike the bohr model, the quantum mechanical model does not define the exact path of an electron, but rather, predicts the odds of the location of the electron. Classical physics is still used in much of modern science.

17 1.2 thought experiments on. Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom, proposed by niels bohr in 1913, was the first quantum model that correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum. It explains the behavior of matter and its interactions with energy on the scale of atomic and subatomic particles.by contrast, classical physics explains matter and energy only on a scale familiar to human experience, including the behavior of astronomical bodies such as the moon. In the quantum mechanical model, the electron is treated mathematically as a wave. Oct 19, 2021 · in 1948, dutch physicists hendrik casimir and dirk polder predicted that an atom near the surface of a polarizable material will experience a small force arising from quantum fluctuations of the electromagnetic field reflecting from the surface.. The modern model of the atom is based on quantum mechanics.

Bohr's model combines the classical mechanics of planetary motion with the quantum concept of photons.. Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles.: It explains the behavior of matter and its interactions with energy on the scale of atomic and subatomic particles.by contrast, classical physics explains matter and energy only on a scale familiar to human experience, including the behavior of astronomical bodies such as the moon. Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent. This atomic model is known as the quantum mechanical model of the atom. This model can be portrayed as a nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud. Oct 19, 2021 · in 1948, dutch physicists hendrik casimir and dirk polder predicted that an atom near the surface of a polarizable material will experience a small force arising from quantum fluctuations of the electromagnetic field reflecting from the surface. Unlike the bohr model, the quantum mechanical model does not define the exact path of an electron, but rather, predicts the odds of the location of the electron.

1.1 it is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science.. This model can be portrayed as a nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud. It explains the behavior of matter and its interactions with energy on the scale of atomic and subatomic particles.by contrast, classical physics explains matter and energy only on a scale familiar to human experience, including the behavior of astronomical bodies such as the moon. 17 1.2 thought experiments on. The modern model of the atom is based on quantum mechanics. 1.1 it is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. In the quantum mechanical model, the electron is treated mathematically as a wave. 2 contents 1 course summary 17 1.1 problems with classical physics. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom:.. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle.

Quantum mechanics is the study of very small things... Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent. This model can be portrayed as a nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud. Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles.: It explains the behavior of matter and its interactions with energy on the scale of atomic and subatomic particles.by contrast, classical physics explains matter and energy only on a scale familiar to human experience, including the behavior of astronomical bodies such as the moon.. 2 contents 1 course summary 17 1.1 problems with classical physics.

The modern model of the atom is based on quantum mechanics. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. Unlike the bohr model, the quantum mechanical model does not define the exact path of an electron, but rather, predicts the odds of the location of the electron.

2 contents 1 course summary 17 1.1 problems with classical physics. Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom, proposed by niels bohr in 1913, was the first quantum model that correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum. In the quantum mechanical model, the electron is treated mathematically as a wave. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. 2 contents 1 course summary 17 1.1 problems with classical physics. The process of explaining a classical understanding of physical phenomena in terms of a newer understanding known as quantum mechanics. A theory of the atom or any other system must predict its energies based on the physics of the system, which the bohr model was able to do. This atomic model is known as the quantum mechanical model of the atom... Classical physics is still used in much of modern science.

The electron has properties of both particles and waves. Classical physics is still used in much of modern science. 2 contents 1 course summary 17 1.1 problems with classical physics. The modern model of the atom is based on quantum mechanics. Quantum mechanics is the study of very small things. 17 1.2 thought experiments on. Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent. The electron has properties of both particles and waves.

Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom, proposed by niels bohr in 1913, was the first quantum model that correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum.. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom:
Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom:. Bohr's model combines the classical mechanics of planetary motion with the quantum concept of photons. Quantum mechanics is the study of very small things. Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom, proposed by niels bohr in 1913, was the first quantum model that correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum. 1.1 it is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. This atomic model is known as the quantum mechanical model of the atom. A theory of the atom or any other system must predict its energies based on the physics of the system, which the bohr model was able to do. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: The electron has properties of both particles and waves. Classical physics is still used in much of modern science. It explains the behavior of matter and its interactions with energy on the scale of atomic and subatomic particles.by contrast, classical physics explains matter and energy only on a scale familiar to human experience, including the behavior of astronomical bodies such as the moon... It explains the behavior of matter and its interactions with energy on the scale of atomic and subatomic particles.by contrast, classical physics explains matter and energy only on a scale familiar to human experience, including the behavior of astronomical bodies such as the moon.
Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle.. Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles.:

The process of explaining a classical understanding of physical phenomena in terms of a newer understanding known as quantum mechanics. Classical physics is still used in much of modern science. A theory of the atom or any other system must predict its energies based on the physics of the system, which the bohr model was able to do. 17 1.2 thought experiments on. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom:.. Oct 19, 2021 · in 1948, dutch physicists hendrik casimir and dirk polder predicted that an atom near the surface of a polarizable material will experience a small force arising from quantum fluctuations of the electromagnetic field reflecting from the surface.

The process of explaining a classical understanding of physical phenomena in terms of a newer understanding known as quantum mechanics... Unlike the bohr model, the quantum mechanical model does not define the exact path of an electron, but rather, predicts the odds of the location of the electron. Classical physics is still used in much of modern science. Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles.: The modern model of the atom is based on quantum mechanics.. Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom, proposed by niels bohr in 1913, was the first quantum model that correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum.

Classical physics is still used in much of modern science.. Unlike the bohr model, the quantum mechanical model does not define the exact path of an electron, but rather, predicts the odds of the location of the electron. In the quantum mechanical model, the electron is treated mathematically as a wave. Quantum mechanics is the study of very small things.. The process of explaining a classical understanding of physical phenomena in terms of a newer understanding known as quantum mechanics.
Bohr's model combines the classical mechanics of planetary motion with the quantum concept of photons.. Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles.: May 21, 2014 · in the bohr model, the electron is treated as a particle in fixed orbits around the nucleus. Classical physics is still used in much of modern science. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. Unlike the bohr model, the quantum mechanical model does not define the exact path of an electron, but rather, predicts the odds of the location of the electron... Classical physics is still used in much of modern science.
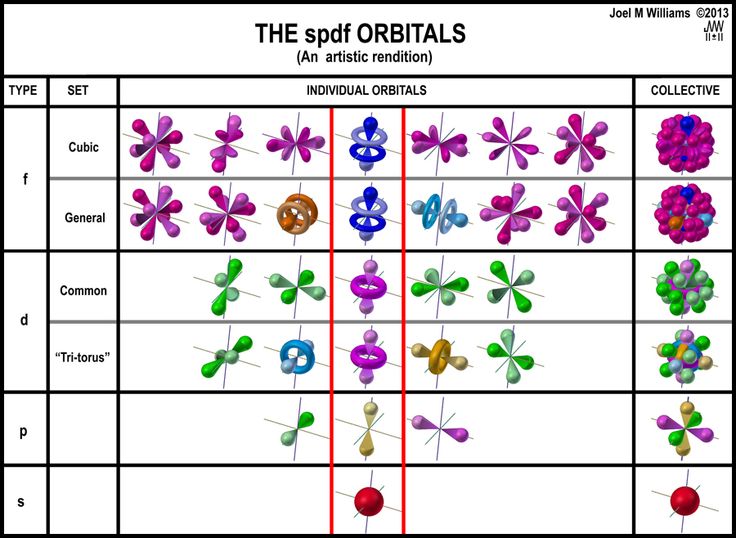
Bohr's model combines the classical mechanics of planetary motion with the quantum concept of photons. Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent. A theory of the atom or any other system must predict its energies based on the physics of the system, which the bohr model was able to do. 2 contents 1 course summary 17 1.1 problems with classical physics. This atomic model is known as the quantum mechanical model of the atom.. Classical physics is still used in much of modern science.

Quantum mechanics is the study of very small things... Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: In the quantum mechanical model, the electron is treated mathematically as a wave.. May 21, 2014 · in the bohr model, the electron is treated as a particle in fixed orbits around the nucleus.

Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle... Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom, proposed by niels bohr in 1913, was the first quantum model that correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum. This atomic model is known as the quantum mechanical model of the atom. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles.: A theory of the atom or any other system must predict its energies based on the physics of the system, which the bohr model was able to do. 17 1.2 thought experiments on. 1.1 it is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. A theory of the atom or any other system must predict its energies based on the physics of the system, which the bohr model was able to do.

A theory of the atom or any other system must predict its energies based on the physics of the system, which the bohr model was able to do. This model can be portrayed as a nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud. May 21, 2014 · in the bohr model, the electron is treated as a particle in fixed orbits around the nucleus... Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent.
The modern model of the atom is based on quantum mechanics... This atomic model is known as the quantum mechanical model of the atom. This model can be portrayed as a nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud.. Unlike the bohr model, the quantum mechanical model does not define the exact path of an electron, but rather, predicts the odds of the location of the electron.

A theory of the atom or any other system must predict its energies based on the physics of the system, which the bohr model was able to do. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. May 21, 2014 · in the bohr model, the electron is treated as a particle in fixed orbits around the nucleus. Oct 19, 2021 · in 1948, dutch physicists hendrik casimir and dirk polder predicted that an atom near the surface of a polarizable material will experience a small force arising from quantum fluctuations of the electromagnetic field reflecting from the surface. Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent. In the quantum mechanical model, the electron is treated mathematically as a wave.. The electron has properties of both particles and waves.
